What Are the Body Extremities

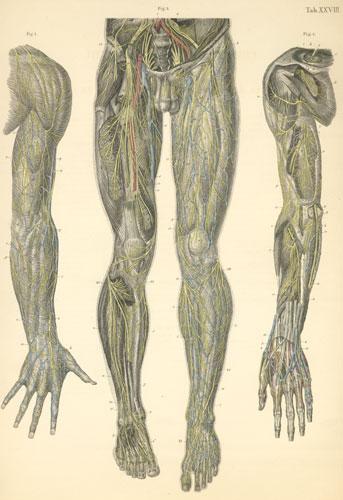
The body extremities are external articulated organs which carry out different locomotoive functions. Humans have four extremities, also known as limbs. On the upper side there are the arms and the lower extremities are the two legs. In the following article on what are the extremities of the human body we explain their functions and components in detail.
Upper extremities: arms
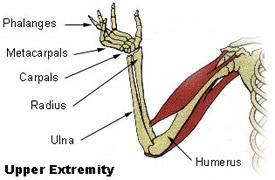
The upper extremities of the human body are arms, which are connected to the upper torso and perform the function of giving mobility to catch, hold and handle objects and perform different activities. The limbs are composed of four parts which are easily distinguished:
- Hand
- Forearm
- Arm
- Shoulder girdle
The upper limbs are attached to the torso and are comprised by two clavicles and two blades. In the arms we can find the humerus, radius and ulna bones and in the hands the carpals, metacarpals and phalanges of the fingers.
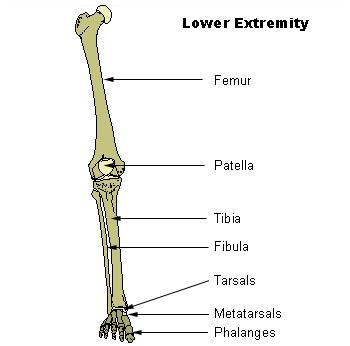
Lower extremities: legs
The lower extremities of the human body are legs, which are attached to the torso at the pelvis through the hip joint. Its functions are supporting the weight of the entire body and allow us to walk, run, jump and ultimately move to any point. The lower limbs are formed by the following parts:
- Thigh
- Leg
- Foot
- Pelvic girdle
The main bones in the lower limb of the human body are the femur, tibia and fibula and the tarsus and metatarsus bones of the foot and the phalanges of the toes.
If you want to read similar articles to What Are the Body Extremities, we recommend you visit our Learning category.